Mission Mission FTX #3 - Team Evaluations - Medical Care/ Buddy Aid/ Evacuating a casualty/ Covering Fire
Situation
"Widowmakers" Platoon, Alpha Company 1-30th Infantry Regiment will move back into Fort Stewart to conduct the first week of their Team level training and evaluations. This phase of the training will cover essential tasks, tactics, and drills for any team (and ultimately squad) to become competent and effective for our future deployments.
Week 2 will focus on medical treatment and pickup procedures, each soldier is expected to know how to administer basic aid and know how to quickly switch to the appropriate communication channels incase of their leadership being knocked unconscious, as well as perform safe casualty relocation and treatment, Platoon and Company staff will evaluate each Squad and their individual teams on these tasks during a live fire exercise to ensure the Saturday training is adhered to. Each Squad will be given objectives and will move on foot from the COP using the techniques they trained on the day prior to display and rehearse their TTPs and internal SOPs.
Mission
"Widowmaker" Platoon conducts dismounted defensive operations in the training area of Ft Stewart on 22 JAN 23 during operation times in order to display their competency, skills, and rehears their internal SOPs to the evaluators. Once complete evaluators will meet with their individual Squads to conduct formal AAR's in order to identify strengths and weaknesses in the tasks of formations, spacing, individual movement techniques, and LDAs.
General Instructions
All information is covered in the Joint Squad SOP at the below link.
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1V9CQNjU6kUbTyOKV0PCGszaHQ_zLn3OwATMgS73Xp8c/edit#
In addition, below are the excerpts specifically covered in the training.
Medical Care
Medical care on the field is critical for saving lives and ensuring the readiness of troops. Combat medics and CLSs are trained to provide immediate care to injured soldiers, including first aid, wound dressings, and basic life support. They are also trained to administer medications and provide other treatments as necessary.
Medical aid is broken into 3 categories
level 1- this is self or buddy aid, this focuses on patching large wounds for self care and patching large wounds and moving casualties to a safe location
level 2- this is CLS specific aid and focuses on stabilizing downed Soldiers. This primarily revolves around a CLS bandaging in a safe area, fixing broken bones, giving fluids and CPR if the Soldier is down. CLS’s can do everything level 1 can do, but adds the ability of giving fluids and focuses on downed members with CPR
level 3- this is medic specific (Squad and then Platoon) and focuses on restoring combat power as quickly as possible. This primarily revolves around all the additional aspects of level 1 and 2 but adds in the ability to stitch. Medics also are the primary establishers of local CCP’s (or Squad CCPs) and will be in a secure location to accept wounded members as they are needed to be tended too.
Usage of bandages

Figure 1. Casualties medical menu.
Use Packing Bandages for Velocity wounds and Elastic Bandages for every other wound. If a wound reopens and there is no medical personnel nearby, use a quickclot. Using the bandages in this order will make sure you have some considerable time before your wounds reopen, serving as a temporary replacement for the stitching kit. If you have a medic nearby, though, don’t use quickclots, ask for a stitch.
Tourniquets

Figure 2. A tourniquet applied to a critically wounded limb
Only placed on a patient’s arms or legs, its purpose is to cut the flow of blood to a specific region, through the application of pressure. / When you find a soldier bleeding out from every body part, the best thing to do if you don’t have any extra hands nearby is to use your tourniquets. First, you will use your tourniquets on all limbs. Then, you will work to close head and chest wounds. They are always the priority. After closing the head and chest wounds, you will proceed to closing all the limb wounds. As soon as you close a wound on a limb, remove the tourniquet right after. It is not recommended that a tourniquet is used for extended periods of time; this can cause severe pain and, if used in multiple limbs at the same time, even death.
CPR
Along with bandaging someone, we also must be aware of their heart rate. If a soldier stays unconscious for exactly 10 minutes without a CPR they will die no matter what else you were doing to avoid that. So always make sure to CPR a downed soldier every 3 to 5 minutes.
Blood status
When pressing H on someone, you will see the medical menu. In the top right corner, you will notice a few phrases with different colors. The first one that will appear is if the soldier is bleeding or not when you click on a body part. Second is generally the blood status. The most common blood status of someone that is down and losing blood, is “lost some blood” with a light yellow color. When you see that, it means you will not require a CLS or medic to bring that soldier back to consciousness. Bandage them up and CPR the soldier until they have a heart rate. After the CPR, check the heart rate and blood pressure.

Figure 3. The medical menu of a casualty displaying "Lost some blood" blood status.
If the blood status is “Lost a lot of blood” in dark orange or worse, you will do the same procedures described above but an epinephrine or morphine will not work because the soldier will need saline first. In this case, you will have to bring the soldier to a CLS or squad medic, so they can finish stabilizing the patient.

Figure 3. The medical menu of a casualty displaying "Lost some blood" blood status.
Correct administration of drugs
As a fireteam member, you will not see numbers when checking for the heart rate or blood pressure. Instead, you will see three different words: Low > Normal > High. After CPRing someone, when you check the heart rate or blood pressure, and it says LOW, use an epinephrine. If it says HIGH, use a morphine. Remember, all of this said above is only applied if there is no medical personnel close to you at all. If there are, always make sure to ask them what to do, and if you use any medication on someone or on yourself, inform your CLSs or squad medic, so they are aware.

Figure 4. The quick view of a casualties medical menu displaying blood pressure.
Buddy aid
If your fellow teammate is wounded, the buddy aid is done in order to stabilize the injuries until more advanced medical care can be provided. All soldiers are trained on buddy aid so even if you are not a CLS, if you have time and are currently in a safe location, by all means you can self-heal, if your wounds are not that bad. If the situation is worse than a simple wound, then the CLS will step in, stabilize the patient and prepare him for transport.
Evacuating a casualty / Covering fire
A correct approach in getting to wounded soldiers is vital in the field of battle. Before rushing to a casualty it is important to assess the situation, most times it is unwise to rush toa downed soldiers aid right away, instead ensuring the trip to and from the casualty is viable. As such each soldier should follow these steps as par TCCC CUF:
1. Evaluate the tactical situation
2. Return fire as necessary, seek cover
3. Alert peers with 3D about contact if necessary, Alert the COC about the casualty
4. Move any injured personnel away from burning buildings or vehicles
5. Move casualty behind hard cover as soon as the tactical situation allows it.
6.Apply tourniquets if necessary
7.Provide treatment to the casualty, hand off the casualty to medical personnel or move the casualty to an established CCP
Special Instructions
(a) MINE DETECTORS: Squad and Fireteam Leaders should use mine detectors at all times due to the risk of anti-personnel mines, IED, and UXO.
(b) DEFUSAL KITS: For defusing explosives noted above (Rangers only).
(c) DEMOLITION CHARGES: M112 Demolition Blocks for destroying enemy caches and other targets as needed (Rangers only).
(d) FIM-92 STINGERS: For destroying enemy aircraft.
(e) FGM-148 JAVELINS: For destroying enemy armor.
Chain Of Command
(a) MISSION: WIDOWMAKER 6, WIDOWMAKER 7, PLATOON HQ PERSONNEL (PRIMARY EVALUATORS)
(b) ADDITIONAL ELEMENTS: WAREAGLE 6, WAREAGLE 7 (ALTERNATE EVALUATORS)
(c) CLOSE AIR SUPPORT: WIDOWMAKER 6, MONEYSHOT
(d) AIR ELEMENTS : FALCON 6 / FALCON 7
Coordination
(a) GROUND-TO-AIR: FREQ LR CH 60, AIR-TO-AIR: FREQ LR CH 61
(b) COMPANY NET: HANDHELD OR LR FREQ 30
(c) PLATOON NET: HANDHELD OR LR FREQ 31
(d) SQUAD NET: HANDHELD FREQ 110/120/130/140
(e) CONVOY NET: FREQ LR CH 33
Intel
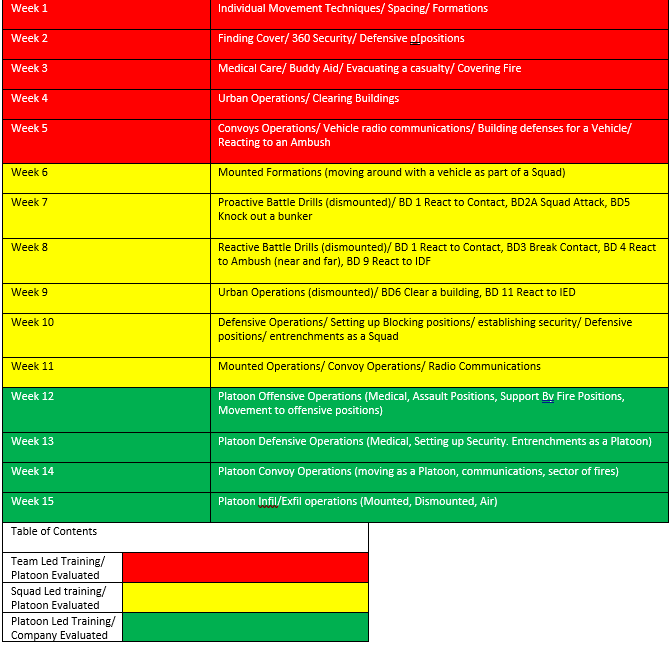
Below is the training schedule until deployment: